Cardiac CT – painless & outpatient
A cardiac CT involves the three-dimensional detection and visualization of the heart and coronary arteries using computed tomography. Coronary heart disease (CHD) can thus be reliably detected or excluded. Since there is no intervention in the patient’s body, the examination is absolutely painless and is performed on an outpatient basis.
max. 20 min
Duration of examination
approx. 45-60 min
Time in practice
Where can you have a cardiac CT performed?
The cardiac CT scan (Cardio-CT-scan) is a modern X-ray diagnostic procedure. It works gently and reliably and is often the best basis for assessing potential heart attack risk. The representation of the Coronary arteries is very detailed. The heart CT is thus a very good alternative to a cardiac catheter examination. Our specialists will explain the details of the examination to you.
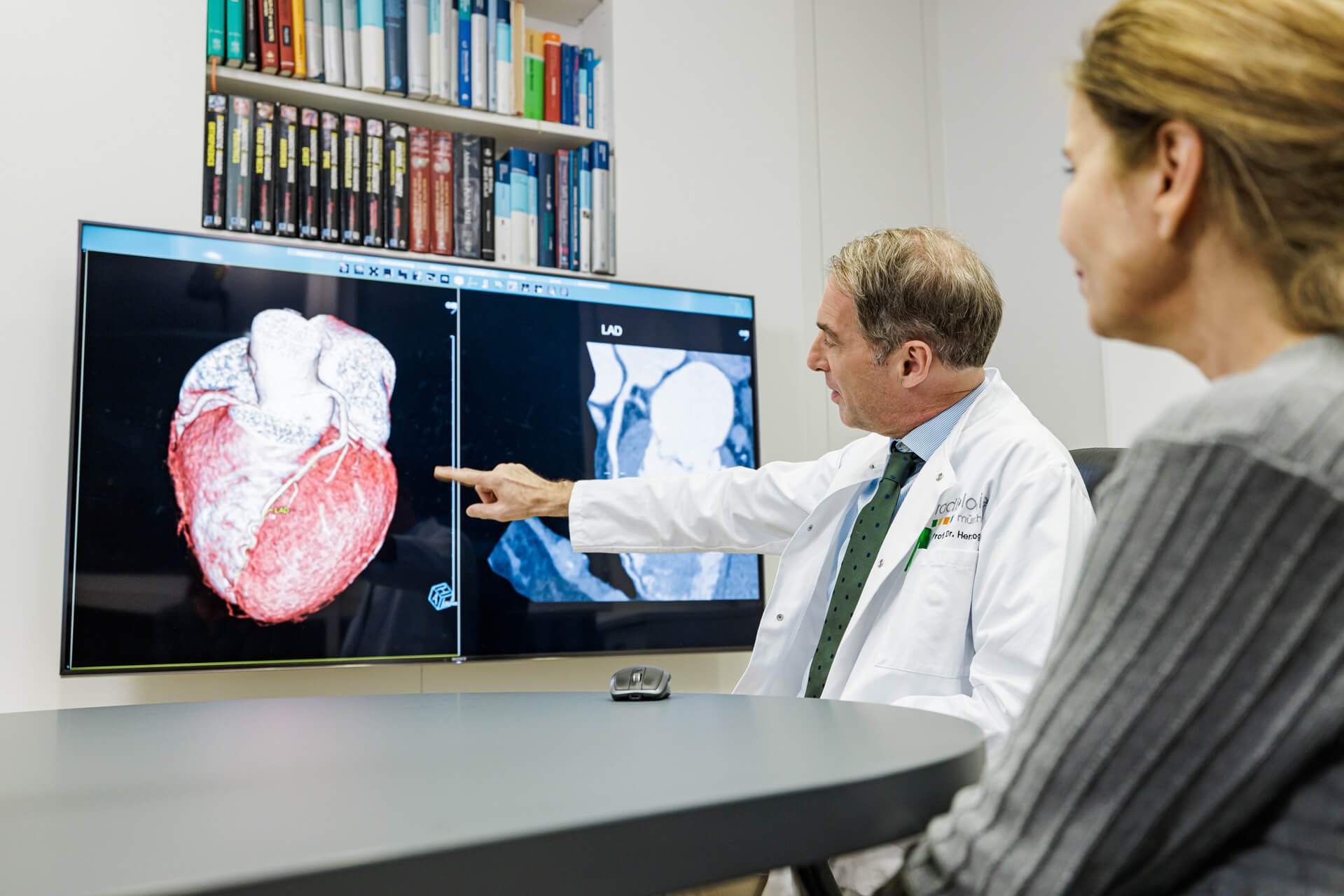
What happens during a cardiac CT?
Computed tomography (CT) can be used to examine the coronary arteries and the heart with high spatial and temporal resolution. The extremely high rotation speed, high-resolution detector configuration, and cardiac (ECG) triggering required for this is only available on the most modern computed tomography scanners that we have in use at Radiologie München.
ECG triggering – controlling the radiation dose by measuring cardiac activity – significantly reduces the radiation dose to be used. In addition, the detectors in the CT have improved considerably in terms of image resolution with the latest generation of technology. Combined with the very high speed of the detectors mentioned above, this ultimately leads to very accurate representations.
Currently, this technique is available to only a few centers worldwide. However, a wide variety of questions can be answered quickly and precisely with cardio-CT. This includes, among other things, the morphological assessment of the heart muscle, heart cavities and valves. However, the focus is on accurate assessment of the coronary arteries.
Who is the heart CT scan suitable for?
Cardiac CT can bring about the diagnosis in patients who suffer from an unclear feeling of tightness in the chest, chest pain, or even shortness of breath during exertion. In contrast to stress ECG or stress scintigraphy, computed tomography detects pathological changes and, in particular, narrowing of the coronary arteries at a very early stage, much earlier than is possible with blood flow tests.
In principle, cardio-CT can also be used in follow-up after stent or bypass surgery. However, close cooperation with the treating physician is required here, since indications may depend directly on the patient’s symptoms, number, size, nature and localization of the stents or bypasses.
What does coronary heart disease (CHD) mean?
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a chronic disease of the coronary arteries caused by atherosclerotic deposits (cholesterol, calcium) on the walls of the blood vessels. This can lead to occlusion and thus interruption of the blood supply to the heart muscle, a heart attack.
Cardiac CT detects coronary heart disease (CHD)
The disease leads to an acute heart attack with fatal consequences in almost every third patient. Clinical symptoms are often atypical or absent. Alternative diagnostic methods, such as stress ECG, scintigraphy, cardiac ultrasound or even laboratory diagnostics, are not very reliable. These map the diseases only indirectly. Only the cardiac CT scan or a cardiac catheterisation examination can directly visualise coronary vessels and atherosclerotic deposits and thus save lives.
What do you need to know before the treatment?
It is important for a cardiac CT scan to be preceded by a laboratory test. We need the current creatinine value and the TSH value. The creatinine value allows conclusions to be drawn about the functioning of the kidney. The TSH describes the functionality of the thyroid gland. Both MUST be checked directly before the examination – at longest one week before. You can also have the values determined by us in advance.
possibly pause antidiabetic drug
Special care should be taken if mild to moderate renal dysfunction is present. If a drug (antidiabetic) with the active ingredient metformin is prescribed for therapy, it would be advisable to take a break two days before the examination. However, this must be done in consultation with the attending doctor. You can find out whether your medicine contains this active ingredient from your doctor, your local pharmacy or from us.
No alcohol, coffee or Viagra before
You should drink plenty of fluids before and also after the examination. This allows the body to excrete the contrast agent more quickly. It is not necessary to abstain from food or drink before the CT scan. However, we ask that you refrain from drinking tea, coffee or alcohol. Male patients are advised to refrain from taking the potency drug Sildenafil (e.g. Viagra) three days before the cardiac CT! Failure to do so may well have life-threatening consequences.
What is the procedure for a cardiac CT?
Decision contrast medium: yes or no
The cardiac CT scan is generally only possible with the administration of a contrast medium. Accurate imaging of the coronary arteries requires administration of the contrast agent via the brachial vein. Only a native CT to determine the calcium content can be performed without such an agent. If there is an allergy or intolerance, we will clarify this comprehensively in advance in a joint discussion.
Keep calm during the examination
After the administration of the contrast agent, it’s time to settle down again. For good images, it is important that the pulse of our patients does not exceed 70 beats per minute during the heart CT scan, if possible. It may therefore be necessary to administer a beta-blocker to lower the pulse before the examination. This is administered to you either in tablet form or intravenously via the arm vein. To check your heartbeat during the CT scan, we connect an ECG beforehand. We administer a nitro spray to dilate the coronary arteries to be examined.
They are then passed through the wide opening of the unit several times. You will lie flat on the mobile examination couch of the tomograph. Via headphones, certain breathing movements are additionally interrogated by our specialist staff. Experience has shown that the so-called flooding of the contrast medium (i.e. the entry into the heart) leads to a strong feeling of warmth – this is completely normal and in no case cause for concern. The individual measurements then always take only a few seconds.
After evaluating the data, our specialists will explain the results to you and provide the images in digital form for the attending physician.
Cardiac MRI
Spatial imaging by means of MRI
Coronary calcium measurement
Detection of calcifications of the coronary arteries
Cardiac diagnostics
Back to the overview of cardiac diagnostics