Lung cancer – not only a problem for smokers
For a long time, bronchial carcinomas were a “men’s issue” – in the meantime, the trend is clearly downward in men, unfortunately, the number of cases in women is slightly upward. Today, about 57,000 patients per year are diagnosed with malignant lung tumours (according to surveys by the Robert Koch Institute). Treatment by chemotherapy or surgery is often combined with adjuvant radiation therapy.
almost 90 % are
Adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and small cell bronchial carcinoma
rd. 20 %
relative survival rate after five years
Smoking
Influences probability of disease
Source: “Cancer in Germany”, RKI/Krebsdaten.de
Where can you have lung cancer treated in Munich?
We now offer the option of starting radiation therapy for lung cancer or metastases in the lungs at three different locations. Select a practice and contact our specialists directly.
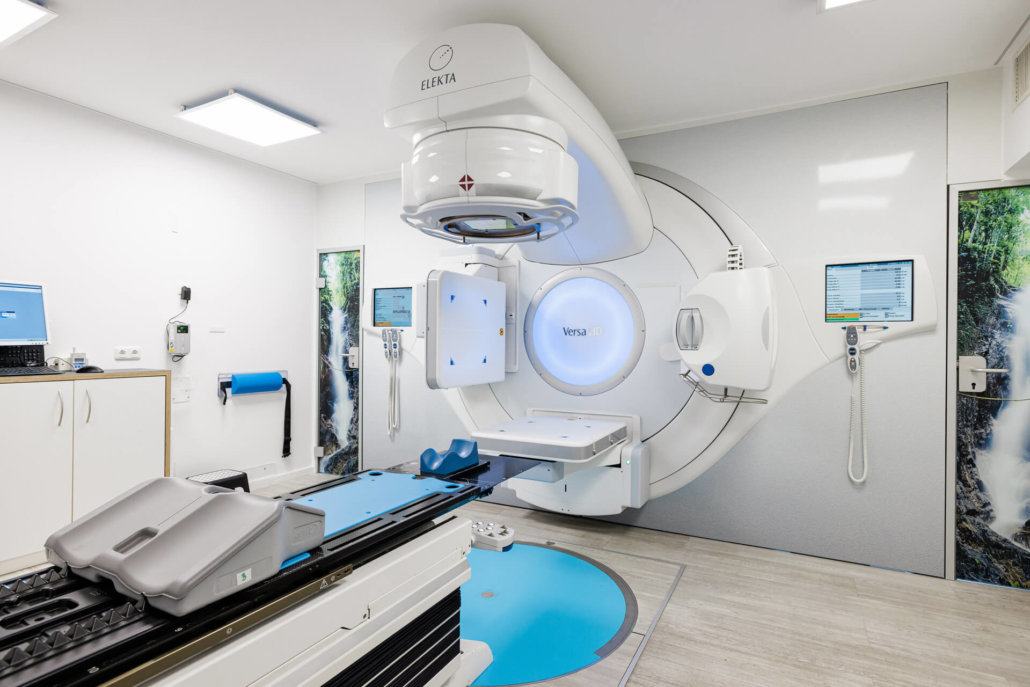
Lung cancer treatment in Munich
Lung cancer (bronchial carcinoma) is one of the most dangerous types of cancer. If this type of cancer is detected during an examination, an individually tailored treatment plan must be developed together with the treating medical team in order to treat the tumor efficiently.
How is lung cancer treated?
In lung cancer, a distinction is made between small-cell and non-small-cell tumours. Depending on the diagnosis, different treatment options may be considered. The position, the spread of the tumour, possible concomitant diseases and the general state of health are also taken into account when choosing the appropriate therapy.
Radiotherapy
In non-small cell lung cancer, radiation therapy or radiochemotherapy is used when the tumor cannot be completely removed surgically. Stereotactic radiotherapy is used in certain cases. In contrast to conventional radiotherapy, the cancer cells are irradiated with a higher dose of radiation that falls off steeply towards the outside, so that the surrounding tissue remains well protected.
In small cell lung cancer, patients are usually treated with radiochemotherapy. In this case, radiation therapy either begins after chemotherapy or the treatment takes place in parallel.
Operation
If the non-small cell tumor is detected early, complete surgical removal can often be promising. Depending on the size and position of the tumor, the affected lung or lungs are removed together with their lymph nodes.
If the stage of the cancer is already advanced or the cancer cells have already affected neighboring organs, surgery is no longer an option. The same is usually true for small cell lung cancer, as this cancer spreads early and metastasizes to other organs.
Chemotherapy/immunotherapy
Chemotherapy and/or immunotherapy are used for non-small cell tumors either in addition to surgery, or when surgery is not possible. In small cell lung cancer, it is the most important treatment method. Treatment with the help of drugs is intended to prevent or at least slow down the spread and invasion of cancer cells from other organs. In certain situations, chemo/immunotherapy is used together with radiotherapy(radiochemo/immunotherapy).
Palliative therapy
If the cancer is already too far advanced or if metastases are detectable in other organs, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy are primarily used to push back the disease. The patient’s quality of life improves as the symptoms are alleviated.
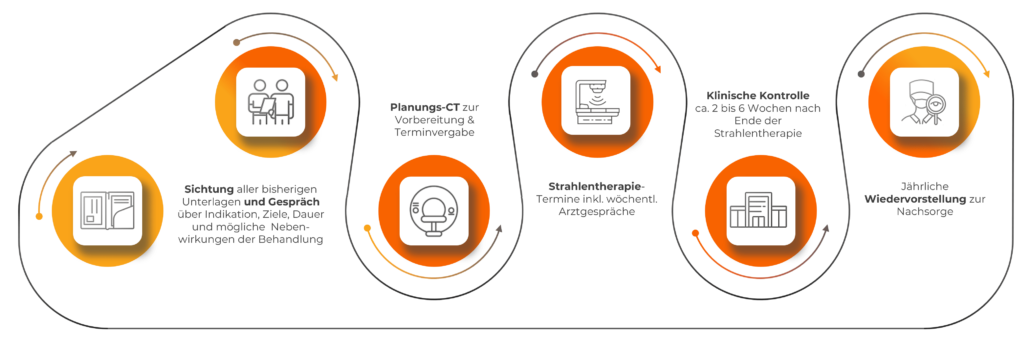
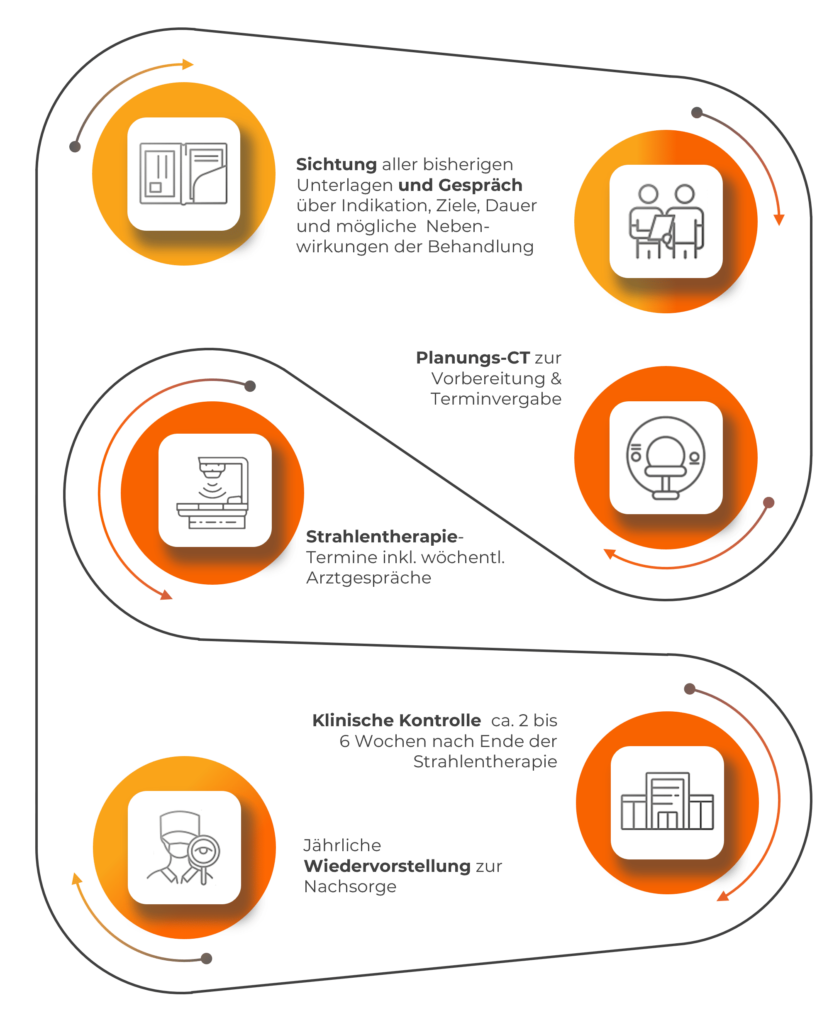
What is the treatment process in our practices?
What do you need to know before, during and after radiotherapy?
Please make sure you eat a healthy, balanced diet and drink enough water. A healthy nutritional status plays an important role in the treatment of the tumor. It also helps reduce the side effects of radiation therapy and improve quality of life.
As radiation can be strenuous and tiring, we advise you not to drive yourself after radiation. Please have someone take you home. The radiology team in Munich will also be happy to organize a cab for you. This is usually covered by your health insurance.
Alcohol and smoking should be refrained from. We also advise against hot and spicy foods. Your radiotherapist will be happy to inform you individually.
What are the side effects of radiation to the lungs?
The treatment plan is individually tailored to the patient so that the cancer treatment is as efficient as possible and the therapy as gentle as possible. However, side effects may still occur during or after treatment. Among other things, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, inflammation of the mucous membranes, skin irritation and weakness may occur. Inflammation of the lungs is rather rare.
All these side effects can be treated and alleviated directly during or after therapy. For this purpose, your attending physician will visit you in our practice at least once a week and will take as much time as necessary in a personal consultation. The side effects usually subside on their own after the end of the therapy due to natural repair processes.